Effects of global warming
Global warming is a term to describe the observed century-scale rise in the average temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere and oceans, which gradually change the Earth’s climate system. Today, we agree that global warming is real and is caused by over-emittance of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide trap heat in the atmosphere that would otherwise escape from Earth. The overuse of fossil fuels and increased human activities in agricultures are believed to be the main source of the global warming over the past 50 years. Human activities release around 37 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide per year. The level of carbon dioxide on earth has increased by 34% since the industrial revolution in 1700.
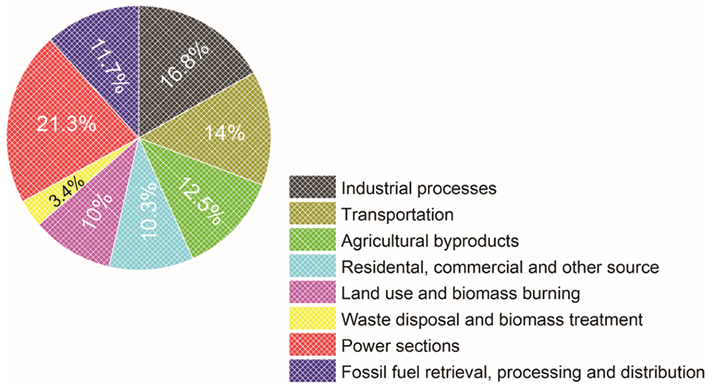
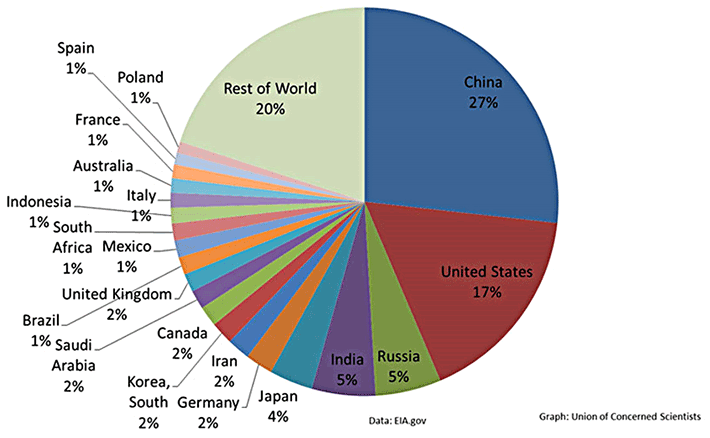
Annual greenhouse gas emission by sector
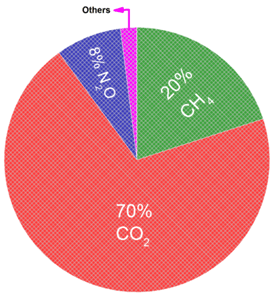
World greenhouse gas emission
Carbon dioxide emissions from the consumption of Energy (2011)
Increase in average temperatures
Today, we can observe the effects of global warming on our planet in a variety of ways. The average temperature of the Earth has increased over the past century; the oceans around the world, including the Pacific Ocean, are warming rapidly. As an example, the average temperature of the Earth has increased between 0.4 and 0.8 °C over the past 100 years. It is predicted that the average temperature will rise by 5.8 degrees by year 2100. In some areas, the rate of increasing temperature is faster than the other regions. According to the multinational Arctic Climate Impact Assessment report collected between 2000 and 2004, the average temperature in Alaska, Western Canada and Russia has risen at twice the global average. More seriously, the heat related deaths increased by more than 2000 percent over the previous decade and will give rise to 150,000 deaths between 2000-2100.
Extreme weather events
Scientists project extreme weather changes around the world. While experiencing some of the hottest summer on record in many countries, some areas also have been experiencing colder than normal winters. Global warming increases the temperature difference between the warm oceans and the cold upper atmosphere, which results more intense hurricanes around the world. Additionally, we observe global warming is likely to bring extreme weather events, such as long droughts in many countries or rainfall and floods in other parts. Climate models forecast that global warming has caused significant changes in climate pattern worldwide.
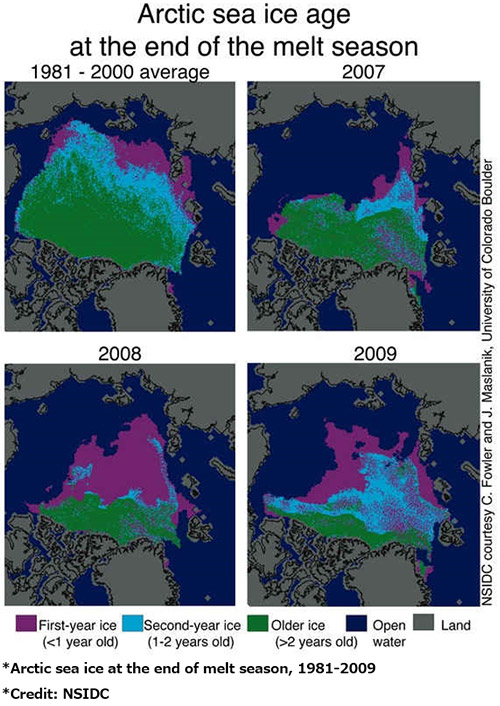
Ice melt
One of the most serious effects of global warming is the reduction of the Arctic ice. In 2012, the smallest amount of Arctic ice cover ever was recorded; unfortunately, the climate models predict that by 2040, the Arctic sea is completely ice free, or even earlier.
Sea levels
Recently, the ocean levels rise significantly with acceleration in melting ice in the Arctic and Antarctic, coupled with melting glaciers in Greenland, Alaska, Europe and Asia. In 2014, the sea level rise accelerated around double as compared to the average annual rise of 0.07 inches per year on average worldwide in 20th century, the World Meteorological Organization reported. Sea levels have risen about 7 inches over the last 100 years, which is more than the previous 2000 years. The major concern is that if current trends continue, it could threaten the lives of people living along the coastal area. It was predicted that sea levels will rise by 7-23 inches by the end of this century, which will be 2.3 feet higher in New York City, 2.9 feet higher at Hampton Roads, and 3.5 feet higher at Galveston, Texas, the EPA report.
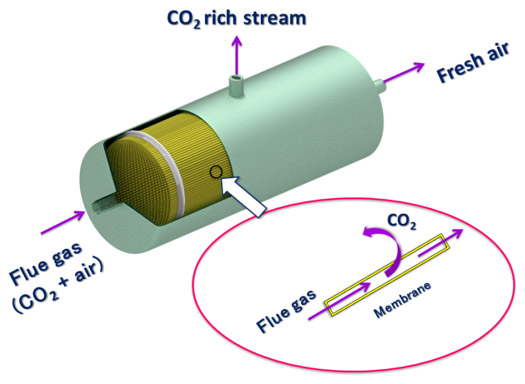
What is membrane? And how can membrane present solutions for the problems of global warming?
A membrane for gas separation is a selective barrier which allows one gas to pass through but stops others. Gas mixtures can be effectively separated by membranes made from organic or inorganic materials. The membranes are normally non-porous and the gas molecules are separated according to their size, diffusivity and solubility.
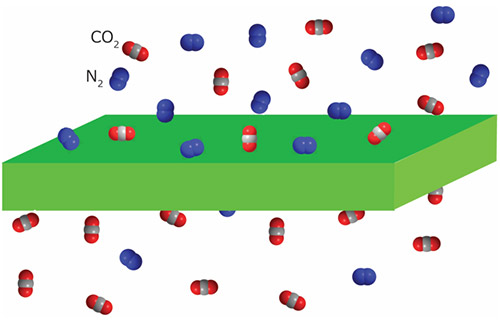
We have the capability to apply ultra-thin film membranes on porous non-selective supports to approach high gas flux with an acceptable selectivity. Membranes with low CO2 permeance require too much membrane area; therefore, using high CO2 permeance (>1000 GPU) membranes are necessary.